- Thyroid
- Thyroid Hormone Profile and Its Prognostic Impact on the Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Korean Patients
-
Jiyeon Ahn, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Seo Young Sohn
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2021;36(4):769-777. Published online August 27, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2021.1109
-
-
4,353
View
-
185
Download
-
17
Web of Science
-
18
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
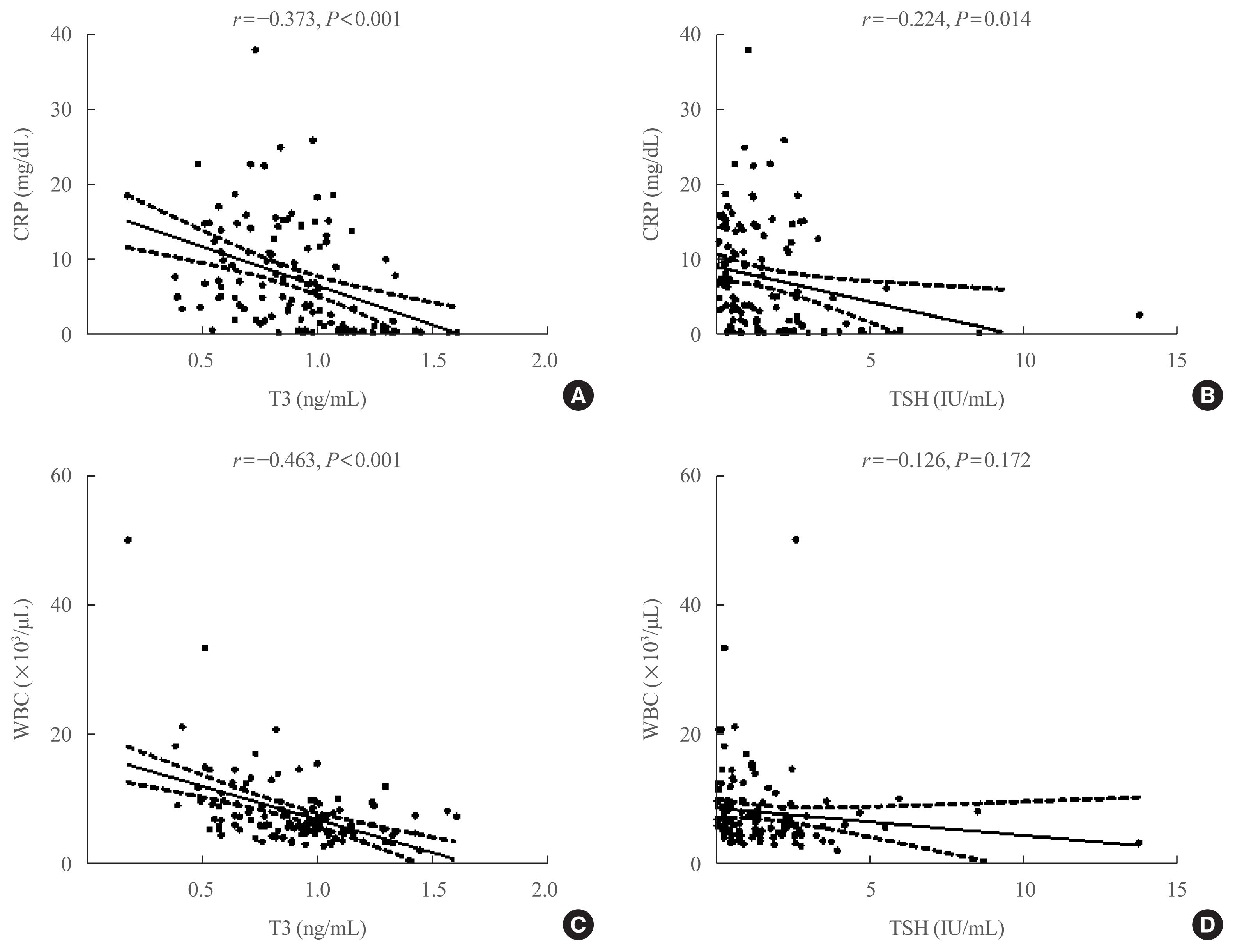
Data on the association between coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and thyroid have been reported, including overt thyrotoxicosis and suppression of thyroid function. We aimed to evaluate the thyroid hormone profile and its association with the prognosis of COVID-19 in Korean patients.
Methods
The clinical data of 119 patients with COVID-19, admitted in the Myongji Hospital, Goyang, South Korea, were retrospectively evaluated. The thyroid hormone profiles were analyzed and compared based on disease severity (non-severe disease vs. severe to critical disease). Clinical outcomes were analyzed according to the tertiles of thyroid hormones.
Results
Of the 119 patients, 76 (63.9%) were euthyroid, and none presented with overt thyroid dysfunction. Non-thyroidal illness syndrome was the most common manifestation (18.5%), followed by subclinical thyrotoxicosis (14.3%) among patients with thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and triiodothyronine (T3) levels were significantly lower in patients with severe to critical disease than in those with non-severe disease (P<0.05). Patients in the lowest T3 tertile (<0.77 ng/mL) had higher rates of mechanical ventilation, intensive care unit admission, and death than those in the middle and highest (>1.00 ng/mL) T3 tertiles (P<0.05). COVID-19 patients in the lowest T3 tertile were independently associated with mortality (hazard ratio, 5.27; 95% confidence interval, 1.09 to 25.32; P=0.038) compared with those in the highest T3 tertile.
Conclusion
Thyroid dysfunction is common in COVID-19 patients. Changes in serum TSH and T3 levels may be important markers of disease severity in COVID-19. Decreased T3 levels may have a prognostic significance in COVID-19 related outcome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The prevalence of thyroid disorders in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sadra Ashrafi, Hossein Hatami, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Mohammad Hossein Panahi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Thyroid Stimulating Hormone as a Possible Additional COVID-19 Outcome Marker
Anamarija Zrilic Vrkljan, Ana Majic Tengg, Tanja Palaversa, Srecko Marusic, Lana Ruzic, Ines Bilic-Curcic, Maja Cigrovski Berkovic
Medicina.2024; 60(2): 314. CrossRef - Effect of Hypothalamic Adrenal Axis and Thyroid Function Alterations on Prognosis of Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients
Muhammet KORKUSUZ, Sulbiye KARABURGU, Tayfun ET, Rafet YARIMOĞLU, Nuh KUMRU
Namık Kemal Tıp Dergisi.2024; 12(1): 17. CrossRef - Thyroxine changes in COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ziqi Li, Pengwei Hou, Shuwen Mu, Renzhi Wang, Hui Miao, Ming Feng, He Wang, Wentai Zhang, Yihao Chen, Tianshun Feng, Shousen Wang, Yi Fang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection on the Thyroid Gland
Aleksandra Piekarska, Marta Góral, Marta Kozula, Aleksandra Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, Katarzyna Zawadzka, Marek Bolanowski
Biomedicines.2023; 11(2): 614. CrossRef - Thyroid Function Abnormalities and Outcomes in Hospitalized Patients
with COVID-19 Infection: A Cross-Sectional Study
Deepika Patel, Dukhabandhu Naik, Sadishkumar Kamalanathan, Kadhiravan Tamilarasu, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Ayan Roy, Chandhana Merugu, Varun Suryadevara
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(03): 169. CrossRef - The Spectrum of Thyroid Function Tests and Autoantibodies During Hospitalization and After Six Months of Discharge in COVID-19 Patients: Does COVID-19 Trigger Autoimmunity?
Ziynet Alphan Uc, Pinar Yagcı, Zelal Adibelli, Cevdet Duran
Endocrine Research.2023; 48(2-3): 44. CrossRef - Transient low T3 syndrome in patients with COVID-19: a new window for prediction of disease severity
Mingyao Zhong, Yue Gao, Hongling Hu, Xuan Zhu, Lulu Gan, Ling Li, Cheng Xiang, Yimin Yan, Zhe Dai
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between COVID-19 and Thyroxine Levels: A Meta-Analysis
Yiru Chen, Xiuneng Li, Yu Dai, Jingjing Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The New Entity of Subacute Thyroiditis amid the COVID-19 Pandemic: From Infection to Vaccine
Mihaela Popescu, Adina Ghemigian, Corina Maria Vasile, Andrei Costache, Mara Carsote, Alice Elena Ghenea
Diagnostics.2022; 12(4): 960. CrossRef - Potential of Endogenous Oxytocin in Endocrine Treatment and Prevention of COVID-19
Stephani C. Wang, Fengmin Zhang, Hui Zhu, Haipeng Yang, Yang Liu, Ping Wang, Vladimir Parpura, Yu-Feng Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between FT3 With the Outcome and Inflammation/Coagulopathy/Fibrinolysis of COVID-19
Jiayi Deng, Siye Zhang, Fei Peng, Quan Zhang, Yi Li, Yanjun Zhong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Primary hypothyroidism with an episode of ventricular tachycardia in a patient with COVID-19
Pin-Hsu Liao, Yu-Cheng Cheng, Po-Yu Liu, I-Te Lee
Medicine.2022; 101(25): e29243. CrossRef - Low triiodothyronine syndrome is associated with stroke‐associated pneumonia
Huijun Chen, Minjie Xu, Yezhi Huang, Jincai He, Wenwei Ren
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of thyroid dysfunction and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Darvishi, Mohammad Reza Nazer, Hamze Shahali, Majid Nouri
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The prognostic utility of serum thyrotropin in hospitalized Covid-19 patients: statistical and machine learning approaches
E. Pappa, P. Gourna, G. Galatas, M. Manti, A. Romiou, L. Panagiotou, R. Chatzikyriakou, N. Trakas, G. Feretzakis, C. Christopoulos
Endocrine.2022; 80(1): 86. CrossRef - Thyrotropin Levels in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019: Assessment during Hospitalization and in the Medium Term after Discharge
Abdallah Al-Salameh, Noémie Scherman, Imane Adda, Juliette André, Yoann Zerbib, Julien Maizel, Jean-Daniel Lalau, Etienne Brochot, Claire Andrejak, Rachel Desailloud
Life.2022; 12(12): 2014. CrossRef - COVID-19 and thyroid function: What do we know so far?
Camila Lüdke Rossetti, Juliana Cazarin, Fabio Hecht, Fabyan Esberard de Lima Beltrão, Andrea Cláudia Freitas Ferreira, Rodrigo Soares Fortunato, Helton Estrela Ramos, Denise Pires de Carvalho
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Clinical Study
- The Association of Overt and Subclinical Hyperthyroidism with the Risk of Cardiovascular Events and Cardiovascular Mortality: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Cohort Studies
-
Seo Young Sohn, Eunyoung Lee, Min Kyung Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(4):786-800. Published online November 25, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.728
-
-
6,040
View
-
288
Download
-
20
Web of Science
-
22
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader  ePub ePub
- Background
Whether hyperthyroidism is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular events remains controversial. We aimed to evaluate the association of overt and subclinical hyperthyroidism with the risk of ischemic heart disease (IHD), stroke, heart failure, and cardiovascular mortality.
Methods
Studies regarding the association between hyperthyroidism and cardiovascular events were searched on PubMed and Embase databases. The cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk was classified as high and low, based on pre-existing diseases, including history of coronary, cerebral, or peripheral artery disease; heart failure; atrial fibrillation; diabetes mellitus; or chronic kidney disease.
Results
Thirty-seven cohort studies were included in this meta-analysis. The pooled hazard ratio for subjects with overt hyperthyroidism compared with the control group was 1.11 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.03 to 1.19) for IHD, 1.35 (95% CI, 1.03 to 1.75) for stroke, and 1.20 (95% CI, 1.00 to 1.46) for cardiovascular mortality. For subjects with subclinical hyperthyroidism, the pooled hazard ratio was 1.24 (95% CI, 1.07 to 1.45) for IHD, when compared with the control group. Subgroup analysis by CVD risk showed that the risk of stroke in overt hyperthyroidism was increased in the low CVD risk group; however, these association was not observed in the high CVD risk group. Similarly, the risk of IHD in subjects with subclinical hyperthyroidism was significantly increased in the low CVD risk group.
Conclusion
Overt hyperthyroidism is associated with increased risk of IHD, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality, and subclinical hyperthyroidism is associated with increased risk of IHD. These associations were particularly observed in the low risk CVD group without underlying CVD.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Trends in Prevalence of Thyroid Dysfunction and its Associations With Mortality Among US Participants, 1988-2012
Xiaowen Zhang, Yong Wang, Hongwei Wang, Xinlin Zhang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e657. CrossRef - Adequacy of thyroid hormone replacement for people with hypothyroidism in real‐world settings: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
Agathoklis Efthymiadis, Matthew Henry, Dimitrios Spinos, Marianthi Bourlaki, Alexandros Tsikopoulos, Angeliki Bourazana, Anastasios Bastounis, Konstantinos Tsikopoulos
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(5): 488. CrossRef - Thyroid Disorders and Peripheral Arterial Disease
Katica Bajuk Studen, Simona Gaberscek, Katja Zaletel, Ales Blinc, Miso Sabovic, Gerit-Holger Schernthaner, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Pier Luigi Antignani, Mojca Jensterle, Dimitri P Mikhailidis, Pavel Poredos
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2024; 22(1): 36. CrossRef - Higher Risk of Incident Hyperthyroidism in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation
Pang-Shuo Huang, Jen-Fang Cheng, Jien-Jiun Chen, Yi-Chih Wang, Juey-Jen Hwang, Cho-Kai Wu, Chia-Ti Tsai
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): 92. CrossRef - Eurasian clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of secondary (symptomatic) forms of arterial hypertension (2022)
I. E. Chazova, N. M. Chikhladze, N. V. Blinova, Zh. E. Belaya, N. M. Danilov, E. M. Elfimova, A. Yu. Litvin, L. Ya. Rozhinskaya, N. Yu. Sviridenko, M. Yu. Shvetsov, V. A. Azizov, E. A. Grigorenko, N. P. Mit’kovskaja, I. I. Mustafaev, A. G. Polupanov, A. S
Eurasian heart journal.2023; (1): 6. CrossRef -
Sympathetic Activation Promotes Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis in a Rabbit Susceptibility Model of Hyperthyroidism-Induced Atrial Fibrillation via the p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway
Jialin Zheng, Shijian Zhao, Qishi Yang, Yantao Wei, Jianmei Li, Tao Guo
Critical Reviews in Eukaryotic Gene Expression.2023; 33(5): 17. CrossRef - Cardiovascular outcomes in subclinical thyroid disease: an update
Matthew D. Ettleson
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2023; 30(5): 218. CrossRef - Lower free triiodothyronine levels are associated with higher all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in people with diabetes-NHANES 2007–2012
Chang Liu, Zhong Xin, Lin Hua
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 202: 110811. CrossRef - Hyperthyroidism
Sun Y. Lee, Elizabeth N. Pearce
JAMA.2023; 330(15): 1472. CrossRef - Is Thyroid Dysfunction Associated with Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysms? A Population-Based, Nested Case–Control Study from Korea
Hyeree Park, Sun Wook Cho, Sung Ho Lee, Kangmin Kim, Hyun-Seung Kang, Jeong Eun Kim, Aesun Shin, Won-Sang Cho
Thyroid®.2023; 33(12): 1483. CrossRef - Risks of suboptimal and excessive thyroid hormone replacement across ages
U. Feldt-Rasmussen, G. Effraimidis, S. Bliddal, M. Klose
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(5): 1083. CrossRef - Association of Mild Thyroid Dysfunction and Adverse Prognosis Among Chinese Patients With Acute ST Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Mei-Fang Li, Ze-Tao Wei, Shuai Li, Qi-Ming Feng, Jing-Bo Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Cardiovascular Effects of Subclinical Hyperthyroidism following Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Ricardo Correa, Ricardo Villela
Clinical Thyroidology.2022; 34(6): 240. CrossRef - Weight Gain and Body Composition Changes during the Transition of Thyroid Function in Patients with Graves’ Disease Undergoing Radioiodine Treatment
Zhenqin Cai, Qiyu Chen, Yan Ling, Henrik Falhammar
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Minor perturbations of thyroid homeostasis and major cardiovascular endpoints—Physiological mechanisms and clinical evidence
Patrick Müller, Melvin Khee-Shing Leow, Johannes W. Dietrich
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of thyroid hormones-induced oxidative stress on cardiovascular physiology
María Laura Barreiro Arcos
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects.2022; 1866(12): 130239. CrossRef - Yearly Incidence of Stroke and Bleeding in Atrial Fibrillation with Concomitant Hyperthyroidism: A National Discharge Database Study
Juqian Zhang, Arnaud Bisson, Grégoire Fauchier, Alexandre Bodin, Julien Herbert, Pierre Henri Ducluzeau, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Laurent Fauchier
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(5): 1342. CrossRef - Platelet abnormalities in autoimmune thyroid diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yu-tian Cao, Kai-yu Zhang, Jing Sun, Yan Lou, Tian-su Lv, Xinyi Yang, Wen-hui Zhang, Jiang-yi Yu, Qi-biao Wu, Xi-qiao Zhou
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Subclinical Hyperthyroidism: A Review of the Clinical Literature
Karen Tsai, Angela M. Leung
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(3): 254. CrossRef - Thyroid and heart, a clinically relevant relationship
G. Corona, L. Croce, C. Sparano, L. Petrone, A. Sforza, M. Maggi, L. Chiovato, M. Rotondi
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(12): 2535. CrossRef - Antithyroid Drug Treatment in Graves’ Disease
Jae Hoon Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 491. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Outcomes in Thyroid Cancer Patients Treated With Thyroidectomy: A Meta-Analysis
Eun Kyung Lee, Hwa Young Ahn, Eu Jeong Ku, Won Sang Yoo, Young Ki Lee, Kee-Hyun Nam, Young Jun Chai, Shinje Moon, Yuh-Seog Jung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Association between Serum Endogenous Secretory Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products and Vertebral Fractures in Type 2 Diabetes.
-
Cheol Ho Lee, Min Kyung Lee, Hyun Jeong Han, Tae Ho Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Se Hwa Kim
-
Endocrinol Metab. 2012;27(4):289-294. Published online December 20, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2012.27.4.289
-
-
1,952
View
-
24
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Patients with type 2 diabetes are known to have an increased risk for osteoporotic fractures compared with non-diabetic subjects. We investigated whether the serum endogenous secretory receptor for advanced glycation end products (esRAGE) or pentosidine was associated with prevalent vertebral fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes. METHODS: We enrolled 140 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (73 men aged 50 or older and 67 postmenopausal women). Lateral X-ray films of the spine revealed prevalent vertebral fractures. The serum concentration of esRAGE and pentosidine were measured. RESULTS: The mean age of all patients was 66.2 +/- 6.5 years and 22% of patients had prevalent vertebral fractures. Serum pentosidine levels were similar between those with and without vertebral fractures. There were no significant correlations between serum esRAGE levels and age, body mass index, duration of diabetes, and hemoglobin A1c. However, patients with moderate or severe vertebral fractures have a lower esRAGE level compared to those without after adjusting for age and gender (0.33 +/- 0.12 ng/mL vs. 0.24 +/- 0.03 ng/mL, P < 0.05). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that patients in the lowest tertile of esRAGE had a higher risk of moderate or severe vertebral fractures (odds ratio, 16.6; 95% confidence interval, 1.4-198.5) than patients in the highest tertile. CONCLUSION: These results revealed that a low esRAGE level was independently associated with moderate or severe vertebral fractures in type 2 diabetic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Letter: The Association between Serum Endogenous Secretory Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products and Vertebral Fractures in Type 2 Diabetes (Endocrinol Metab 2012;27:289-94, Cheol Ho Lee et al.)
You-Cheol Hwang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(1): 76. CrossRef
- A Case of Complete Agenesis of the Dorsal Pancreas in a Patient with Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus.
-
Dong Pil Kim, Kang Seo Park, Dong Sun Kim, Bong Suk Ko, Ji Hae Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jong Ho Shin, Byung Jun Kim, Hyun Jin Kim
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2010;25(1):78-83. Published online March 1, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2010.25.1.78
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Agenesis of the dorsal pancreas is a rare congenital anomaly caused by underdevelopment or agenesis of the dorsal pancreatic bud that forms the upper head, neck, body and tail of the pancreas. We report a case of agenesis of the dorsal pancreas, which was found under examination of diabetes mellitus (DM). A 16-year-old girl was transferred to our hospital because of a positive urine glucose reading during a school-conducted examination. Abdominal computed tomography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed the deficit of the pancreatic body and tail. Diabetes-associated autoimmune antibodies were negative in a blood test. Decreased beta-cell function was demonstrated by oral glucose tolerance and glucagon stimulation tests. Although the notion that agenesis of the dorsal pancreas leads to decreased endocrine or exocrine function is controversial, the results of this study suggest that we should consider these causes of diabetes mellitus. When treating a young patient with diabetes mellitus, we should consider causes of diabetes mellitus such as congenital anomaly or maturity onset diabetes, in addition to type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Effect of Fenofibrate and Exercise on Metabolic Syndrome and Hepatic Steatosis.
-
Bong Soo Cha, Jae Hyuk Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2007;22(3):188-191. Published online June 1, 2007
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2007.22.3.188
-
-
1,670
View
-
20
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Minireview: A Need for an Adequate Diet Program for Postmenopausal Women with Obesity in the Republic of Korea
So Hee Park, Bo Dam Kim, Jae Hong Sang, Hae-Hyeog Lee, Tae-Hee Kim
Journal of Menopausal Medicine.2023; 29(2): 45. CrossRef
- A Case of Tracheal Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Presenting with Diffuse Goiter.
-
Ho Cheol Kang, Seong Kyun Kim, Se Hoon Kang, Kyung Min Kim, Se In Hong, Dong Jin Chung, Min Young Chung, Joon Kyoo Lee, Sang Chul Lim, Jae Hyuk Lee
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 2005;20(3):273-277. Published online June 1, 2005
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/jkes.2005.20.3.273
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- A goiter is among the most common presenting symptoms of patients with thyroid diseases and is usually caused by intrinsic thyroid problems. While direct invasion of the trachea by aggressive thyroid tumors is a well-known phenomenon, the reverse situation, that is, a primary tracheal neoplasm invading by direct extension into the thyroid gland, presenting with a goiter is very rare. Here, a case of a tracheal adenoid cystic carcinoma(ACC), presenting with a diffuse goiter, is reported. A 47-year-old woman presented with slowly growing anterior neck swelling. A physical examination showed a diffuse firm goiter. The patient was euthyroiditic, and serum negative for thyroid autoantibodies. Thyroid ultrasonography and neck CT revealed a doughnut-shaped mass, encircling the trachea and displacing the thyroid anteriorly. Ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration(FNA) was compatible with an ACC, and a subsequent surgical resection confirmed the diagnosis. Although the occurrence of a tracheal ACC invading the thyroid is rare, this case highlights the need to be aware of unusual lesions arising in the region of the thyroid. This knowledge will help in making the correct cytological diagnosis when these lesions are sampled by FNA
- Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms and Bone Mineral Density in Korean Women.
-
Jae Hong Park, Dong Jin Chung, Jung MIn Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Myung Soo Kim, Seung Won Yang, Min Young Chung, Tae Hee Lee, Jong Tae Park, Min Young Lee, Jae Hyuk Lee, Chan Choi
-
J Korean Endocr Soc. 1998;13(3):394-409. Published online January 1, 2001
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- BACKGROUND
Bone mineral density(BMD) is thought to be under genetic control. Polymorphisms at the vitamin D receptor(VDR) gene have recently been shown to contribute to the genetic variability in bone mineral density in Caucasians. However, the relationship between VDR-RFLP(restriction fragment length polymorphisms) and bone mineral density is controversial. METHODS: The VDR-RFLP by BsmI, ApaI, and TaqI were studied in 250(77 premenopausal, 173 postmenopausal) Korean women. Bone mineral densities at the lumbar spine(L2-L4), femoral neck, greater trochanter, and Wards triangle were measured by DEXA(Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry; Lunar DPX-L, U.S.A.). RESULTS: There were significant differences in VDR gene allele frequency when compared with those in Caucasians. The BsmI polymorphism was consisted of 0.8% BB homozygotes, 12.4% Bb heterozygotes, and 86.8% bb homozygotes. The ApaI polymorphism was 6.8% AA homozygotes, 42.0% Aa heterozygotes, and 51.2% aa homozygotes, and the TaqI polymorphism was 83.2% TT homozygotes, 16.8% Tt heterozygotes, and 0% tt homozygotes. When these three VDR-RFLP were combined, bbaaTT(51.2%), bbAaTT(29.6%), and BbAaTt(10.0%) were found to be most frequent types. There were no significant relationship between VDR-RFLP and BMD measured at the 2nd to 4th lumbar spine in all subjects. But there were significant relationship between VDR-RFLP and BMD at the proxmial femur in all subjects. Compared with bb or bbaaTT(or bbAaTT), women with the Bb or BbAaTt genotypes had significantly lower bone mineral densities at the proximal femur in all subjects. When we restricted the analysis to early postmenopausal women less than 10 years since menopause, these findings were more pronounced. CONCLUSION: These results suggest that VDR-RFLP may affect on BMD at the proximal femur in Korean women. However, the frequencies of B, A, and t alleles are very low in Korean women compared to those of Caucasians, further studies will be needed, with larger sample sizes.
|